-
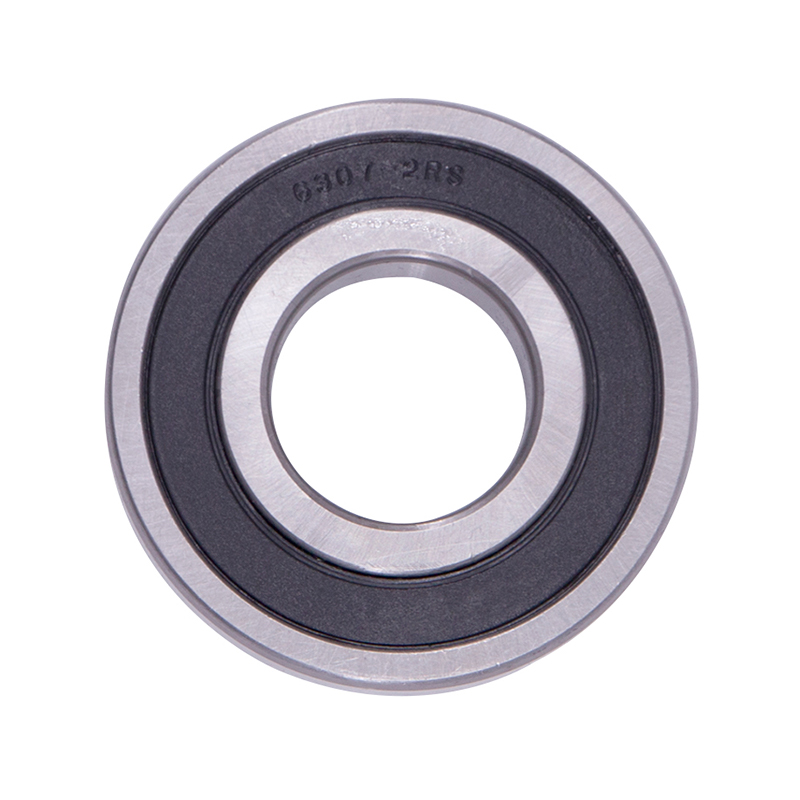 Wheel Hub Bearings
Wheel Hub Bearings -
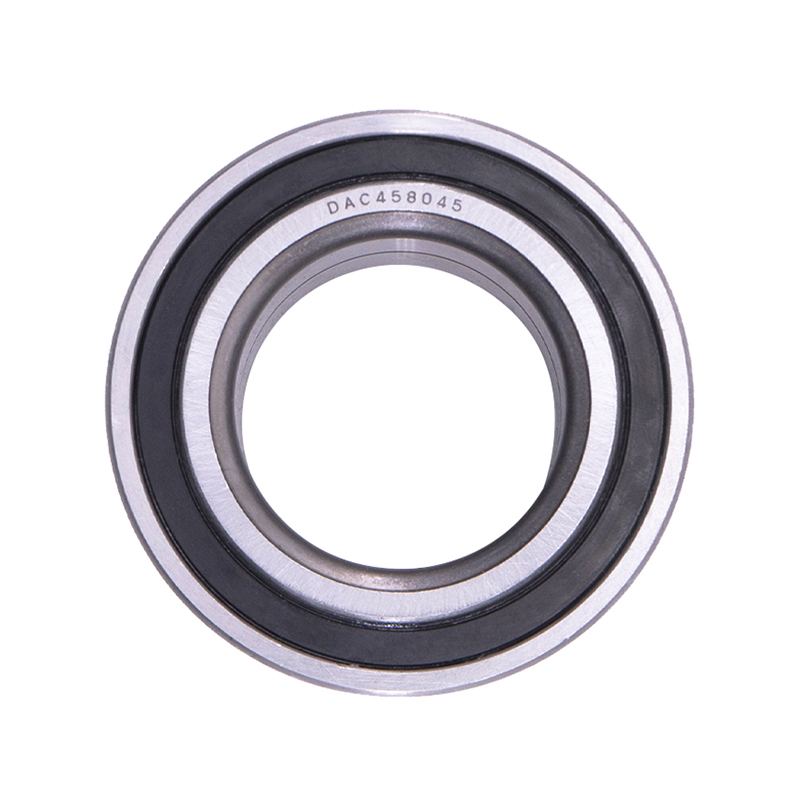 Wheel Hub Bearings
Wheel Hub BearingsDAC387436 DAC458045 Hub Deep Groove Ball Car Wheel Bearing
-
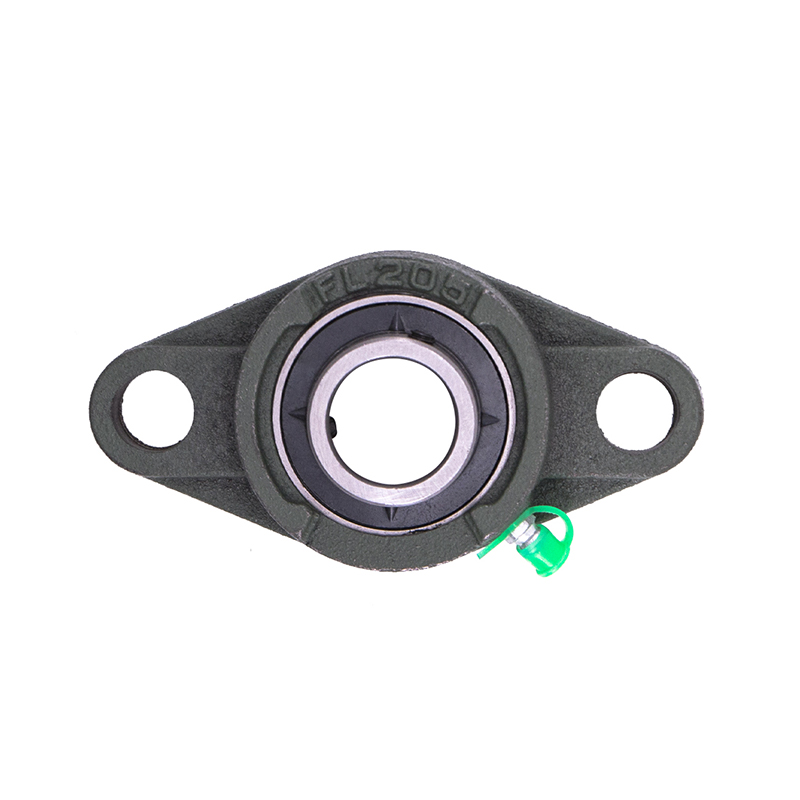 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsFL204 FL205 FL206 Stainless Steel Pillow Block Bearing
-
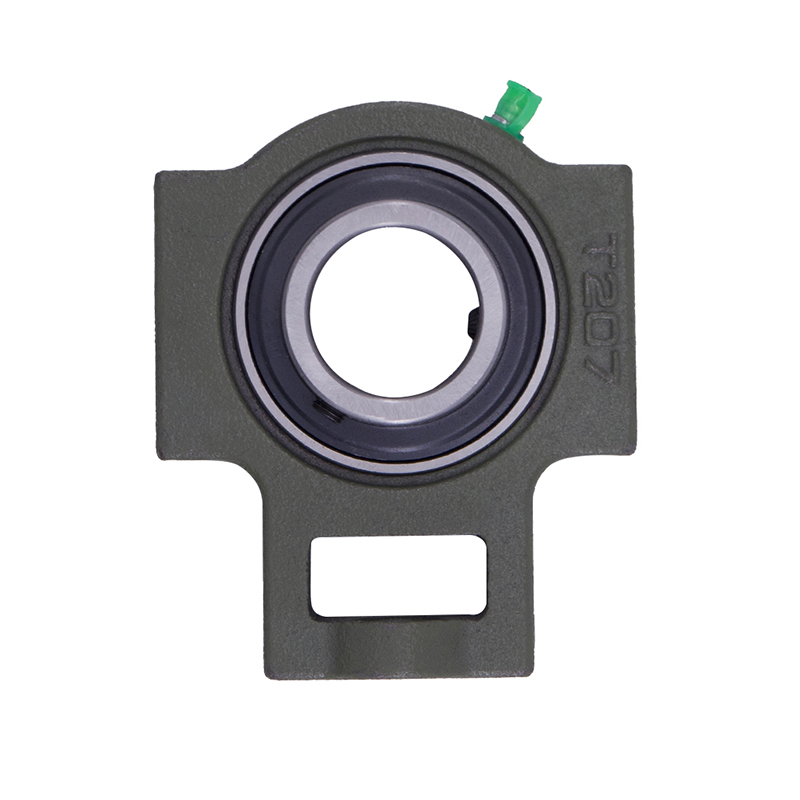 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsT204 T207 UC204 High Speed Insert Pillow Block Bearing
-
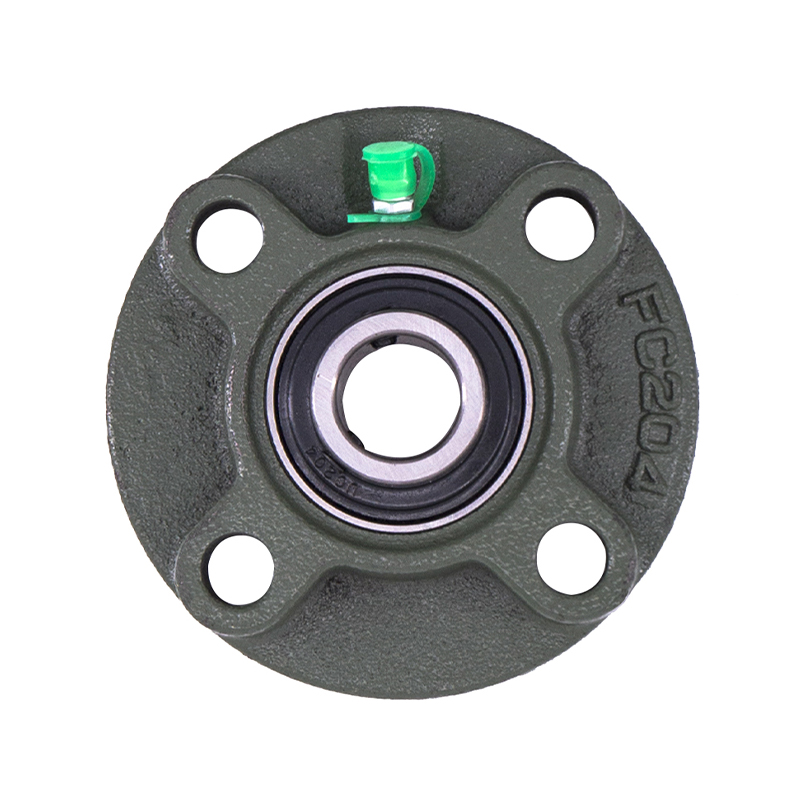 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsFC204 F210 Auto Wheels Bike Pillow Block Bearing
-
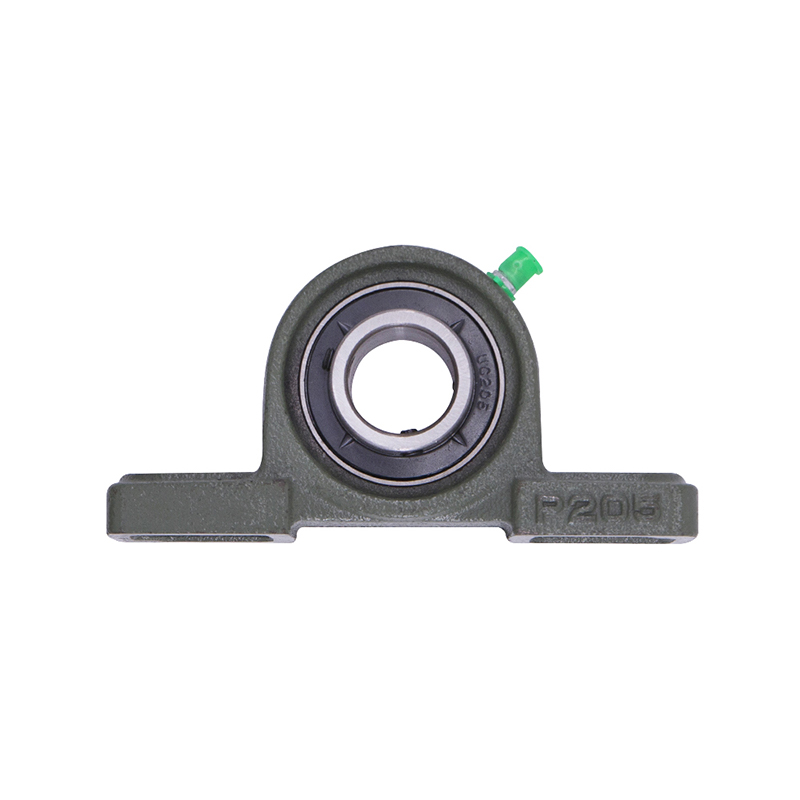 Spherical Bearings
Spherical BearingsP207 206 205 203 High Precision Wheel Pillow Block Bearing
-
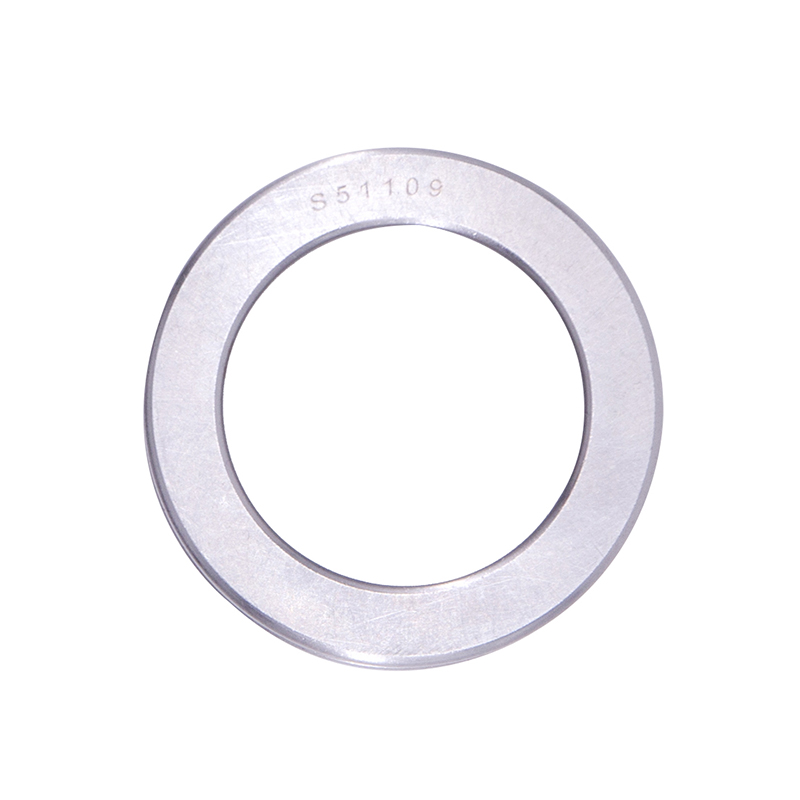 Thrust Roller Bearings
Thrust Roller BearingsS51100 S51107 S51109 Car Wheel Plain Thrust Ball Bearing
-
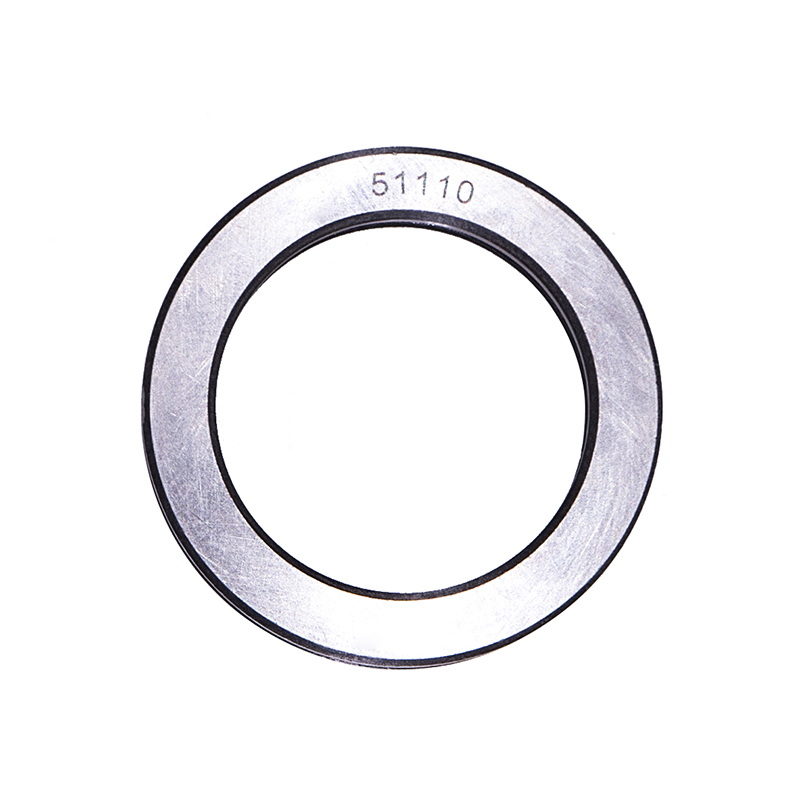 Thrust Roller Bearings
Thrust Roller Bearings51110 51107 51104 51206 High Speed Plain Thrust Ball Bearing
Static and Dynamic Load Ratings of Radial Taper Thrust Roller Bearings
Industry news-Radial taper thrust roller bearings are crucial components in many industrial applications due to their ability to handle both radial and axial loads effectively. Understanding the static and dynamic load ratings of these bearings is essential for selecting the right bearing for specific applications and ensuring their performance and longevity.
The static load rating of radial taper thrust roller bearings refers to the load the bearing can withstand while stationary without causing permanent deformation of the rolling elements or raceways. This rating is crucial for applications where the bearing might be subjected to heavy loads or shock loads while not in motion. The static load rating is determined by the stress that the bearing materials can endure without yielding.
The static load rating is important for ensuring that the bearing can handle peak loads that may occur during equipment startup, shutdown, or unexpected shocks. Selecting a bearing with an appropriate static load rating helps prevent permanent deformation and ensures the bearing maintains its functionality and precision.
The dynamic load rating of radial taper thrust roller bearings is the load the bearing can handle while in motion. This rating is critical for applications where the bearing operates under continuous or fluctuating loads. The dynamic load rating is calculated based on the bearing's ability to withstand a specified number of rotations without experiencing fatigue failure.
The dynamic load rating is influenced by factors such as the material properties, bearing design, lubrication, and operating conditions. It provides a measure of the bearing's durability and its ability to perform reliably under varying load conditions over time. Selecting a bearing with an appropriate dynamic load rating ensures that the bearing can handle the operational loads without experiencing premature wear or failure.
Bearing Life Calculation of Self-Aligning Tapered Roller Bearings
Self-aligning tapered roller bearings are designed to accommodate misalignment and provide reliable performance in various applications. Calculating the bearing life of these bearings is essential for predicting their durability and planning maintenance schedules. The bearing life calculation involves several factors, including load, speed, lubrication, and operating conditions.
The basic bearing life equation, also known as the L10 life, estimates the number of revolutions or operating hours at which 90% of a group of identical bearings will still be operational. The L10 life equation is given by:
L10L10 is the bearing life in millions of revolutions.
CC is the basic dynamic load rating.
PP is the equivalent dynamic bearing load.
pp is the life exponent (typically 3 for ball bearings and 10/3 for roller bearings).
Factors Influencing Bearing Life
Several factors influence the bearing life calculation of self-aligning tapered roller bearings:
Load: The applied load significantly impacts bearing life. Higher loads result in reduced bearing life, while lower loads extend it. Accurately determining the equivalent dynamic load (P) is crucial for precise life calculations.
Speed: Operating speed affects the bearing life by influencing the internal friction and heat generation. Higher speeds can reduce bearing life due to increased wear and potential lubricant degradation.
Lubrication: Proper lubrication is essential for reducing friction and wear, thereby extending bearing life. The type, quantity, and quality of the lubricant, as well as the lubrication method, play a significant role in bearing performance.
Operating Conditions: Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, contamination, and vibration can impact bearing life. Bearings operating in harsh conditions may require more frequent maintenance and lubrication to achieve their expected lifespan.
Alignment and Installation: Self-aligning tapered roller bearings are designed to accommodate misalignment, but excessive misalignment or improper installation can still reduce bearing life. Ensuring proper installation and alignment helps reduce bearing performance.

 English
English русский
русский Español
Español
